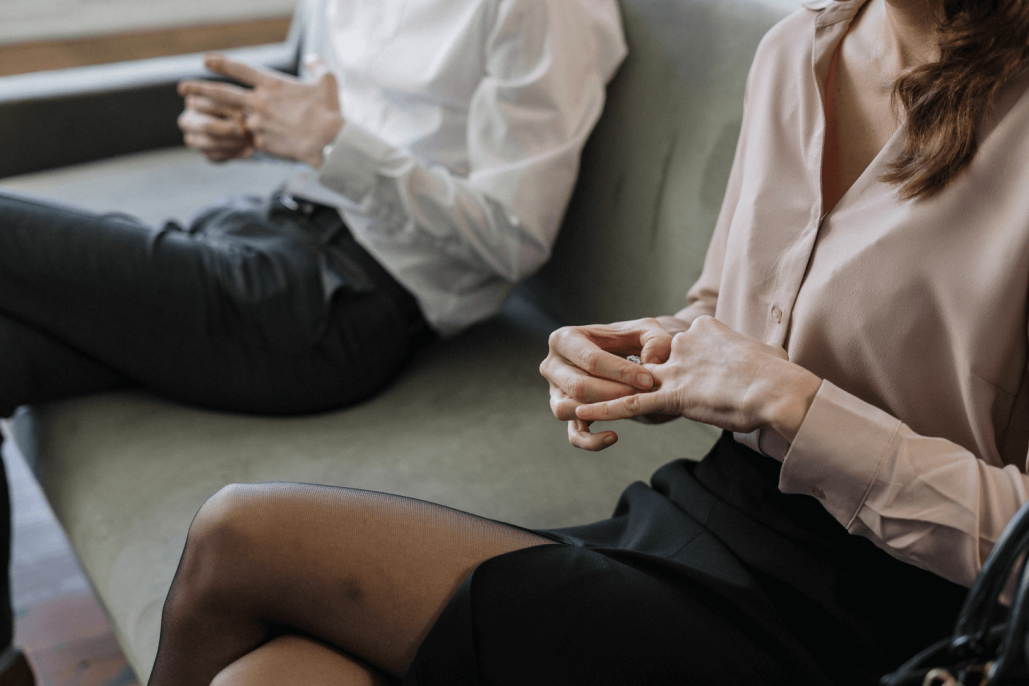
If you’re thinking about starting therapy sessions, you're probably wondering how to find the therapist and therapeutic approach that's best for you.
When considering the different kinds of therapy, you may be thinking:
"Which kind of therapy will get me results?"
What's the best type of therapy?
What are the different therapy approaches?
Which kind of counseling will get me results?
Read on, and we'll share examples of the most common kinds of therapy along with who may benefit most from each approach.
While there won’t be a pop quiz at the end, finding out about the different therapeutic methods might help you determine the therapy approach best-suited for your needs.

How to find the right therapist and kind of therapy
Finding the right therapist for you is essential.
The Monarch Directory by SimplePractice can help you find licensed mental health professionals near you, and quickly and easily book a therapy session—in-person or online telehealth video therapy.
Psychologists, counselors, and therapists may try several therapeutic approaches to find the specific type or blend of therapies that help each client best address their specific needs.
"What's the best type of therapy?"
And, while discovering the optimal therapeutic approach for your needs can be key to your treatment, it's OK if you don't know anything at all about the different modalities and approaches available.
You shouldn't need to be a Psychology major to find a therapist and book a therapy session.
Below we'll demystify some of the most popular types of therapy, so that you have a better idea how they each work and which types of concerns they typically have the most success addressing.
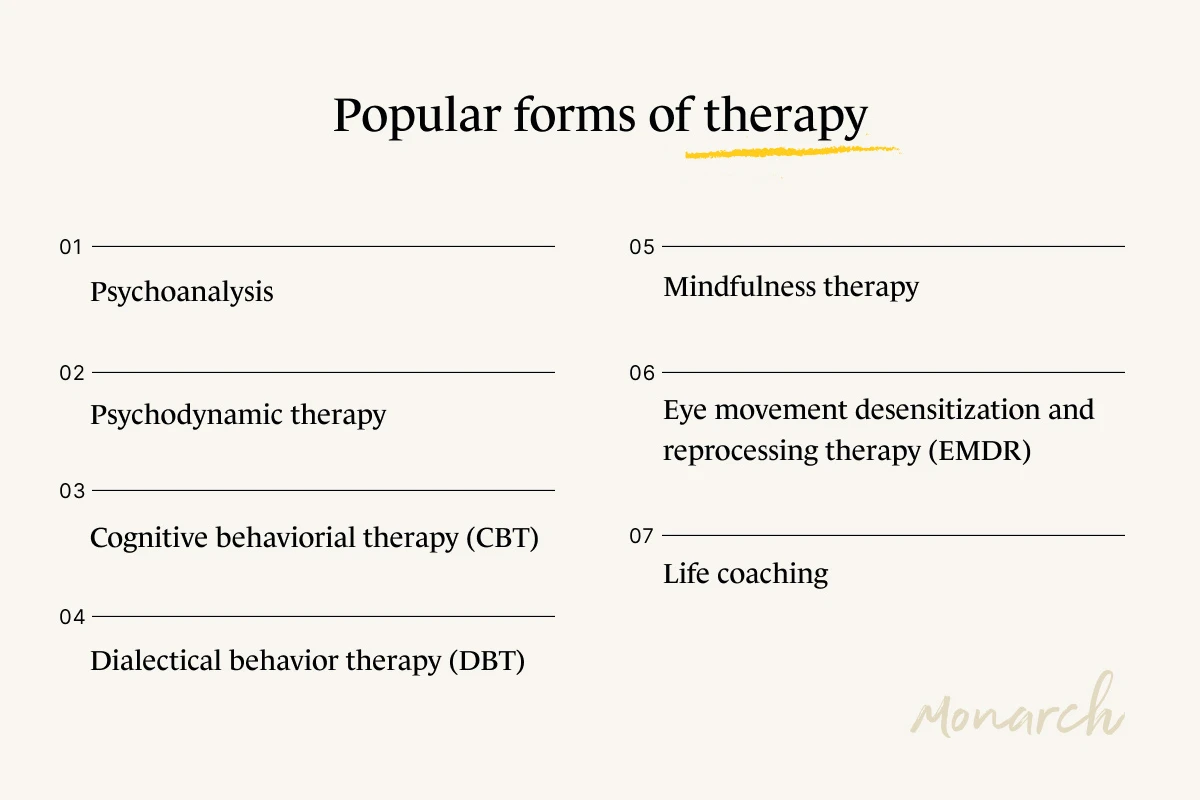
7 types of therapy
There are many styles of therapy—from psychoanalysis and psychodynamic therapy, to cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) to mindfulness-based therapy (MBT), and EMDR (eye movement desensitization and reprocessing).
Let's take a look at some common kinds of therapy and how they work.

1. Psychoanalysis
What is it? Psychoanalysis is talk therapy treatment.
Who's it for? Talk therapy is beneficial for anyone who wants to develop a better understanding of themselves and their motivations.
Psychoanalytic therapy is the kind of talk therapy almost always depicted on television—think the leather couch and the white-bearded doctor or the kindly woman sitting in a chair taking notes, like on The Sopranos.
It's the most influential form of behavioral therapy, and it provided the blueprint for many of the branches that followed.
Psychoanalysis was developed by famous neurologist and psychologist Sigmund Freud in the late 1800s.
"What are the different therapy approaches?"
Freud believed our minds function on three different levels: the conscious, the preconscious, and the unconscious.
He argued that psychological problems are a result of tensions between these different parts of our minds.
When unhealthy thoughts or motivations live in our unconscious and preconscious, according to Freud, our conscious mind suffers too.
Freud’s solution was to make our conscious minds aware of the issues lurking below by way of interrogation, conversation, free association, and the interpretation of dreams and memories.
His methods were specifically designed to dredge up repressed trauma, hidden beliefs, and questionable desires so that they could be addressed by the better-behaved parts of our brains.
So, beyond this history lesson about Freud, how and why does talk therapy work?
Psychoanalytic therapy can involve dream interpretation and free association.
Psychoanalysis still relies heavily on the methodology Freud laid out, however it has certainly come a very long way since the 1800s.
Mental health therapists make a distinction between Freudian, Jungian, and modern psychoanalysis for that very reason.
In psychoanalytic therapy, counselors challenge patients to delve deeper into parts of their mind and life they haven’t yet explored, which can feel a bit rough at times.
Patients undergoing psychoanalysis rely upon their therapists to steer the discussion.
Psychoanalytic therapy can involve dream interpretation and free association.
Therapists help clients interpret their life events, memories, beliefs, and dreams as they come up.
Psychoanalysis is often used in tandem with some of the other therapeutic methods described below.
Check out Monarch by SimplePractice to find a licensed talk therapist near you.

2. Psychodynamic therapy
What is it? A more open-ended talk therapy that involves clients' free association.
Who's it for? Psychodynamic therapy can help people suffering from depression, anxiety and panic disorder, and it can also be helpful for couples and families.
Psychodynamic therapy was developed as a more efficient form of psychoanalysis.
This type of therapy places a strong emphasis on recognizing recurring thought patterns. Patients are again asked to discuss our relationships with other people and to explore our emotions and behavior in these relationships.
Through identifying patterns in our thinking, a psychodynamic approach can help us learn to identify unhealthy coping strategies and defense mechanisms.
For example, we may begin to notice that we always accept blame for problematic situations, even when others are responsible.
Once these habits are observed, the idea is that we can address the symptoms directly without getting as caught up in the interpretation of root causes.
By getting to know the patterns in our thinking, a psychodynamic approach can help us learn to identify unhealthy coping strategies and defense mechanisms.
In this way, psychodynamic therapy is more streamlined and less interpretative than psychoanalysis. It’s also more interactive and goal-oriented in nature.
Treatment plans, with short- and longer-term goals are built to resolve specific issues.
Because psychodynamic therapists rely upon interaction to tease out underlying thought patterns, couples and families may find psychodynamic therapy particularly helpful.
View therapists near you who specialize in a psychodynamic approach.

3. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
What is it? CBT focuses on how our thoughts and beliefs can influence our feelings and behavior.
Who's it for? Adults with ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Anyone with negative thoughts, emotions, and/or behaviors can benefit from CBT. And, CBT-I has been proven to help people with insomnia and sleep issues.

Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is founded on the idea that our perceptions influence our behavior. How we perceive determines how we act.
The premise of CBT is that when we perceive events through a negative lens, we can end up letting everyday events and occurrences cause emotional suffering.
“Cognitive errors,” such as focusing on failure or interpreting another person’s genuine mistake as a personal affront, create a cycle of negative reinforcement that can lead to distress or—in pronounced cases—even mental illness.
Cognitive behavioral therapists have developed techniques that allow patients to adjust their perceptions through practice.
Tools including journaling, thinking exercises, and relaxation techniques, enable patients to catch themselves interpreting their actions or the actions of others through a negative lens, to challenge that perception or belief with other logical conclusions—and eventually—to change their emotional responses.
Over time, patients learn to correct their cognitive errors in perception and—in the process—rid themselves of unnecessary emotional suffering.
CBT is collaborative, and it's designed to resolve specific issues that patients and practitioners identify together as a team.
Cognitive behavioral therapists give plenty of assignments and ask patients to monitor their thoughts and emotional responses to those thoughts on a daily basis.
Patients learn to correct their cognitive errors in perception and rid themselves of unnecessary emotional suffering.
An active commitment to the techniques your therapist shares is critical to the success of cognitive behavioral therapy.
Find a therapist near you who specializes in cognitive behavioral therapy.
4. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
What is it? DBT was created in the 1980s as a modified version of CBT.
Who's it for? Initially developed for clients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) has been shown to have evidence-based benefits for individuals with eating disorders, suicidal behavior, self-harming behaviors, addiction issues, and PTSD.
DBT is an adapted form of cognitive behavioral therapy.
If you want to gain more acceptance and awareness of yourself and others, DBT may be the right type of therapy for you.
DBT therapists work with patients to increase their skills that help them to regulate their emotions.
"Although it may take a bit of time and a great deal of practice to master DBT skills, the outcome of clients being able to self-regulate, improve relationships, and deal with life is immeasurable," says therapist Ellen Biros MS, LCSW, C-PD.
Browse profiles of licensed therapists who specializes in DBT.

5. Mindfulness therapy
What is it? Mindfulness is the practice of being present and detaching from distractions and the triggers that cause you distress.
Who's it for? MBT or mindfulness-based therapy is for people who have difficulty coping with stress and/or staying grounded.
Proponents of mindfulness therapy believe that our minds function on two levels: “being” mode and “doing” mode. They argue that switching between these modes is the key to good mental health.
“Being” mode is a meditative state of simply existing that offers safe detachment from thoughts and actions.
When we're engaged in only being, we afford ourselves a healthy distance from the things that make us anxious or depressed.

The goal of mindfulness therapy is to help patients practice this state of being through meditation and breathing and mindfulness exercises.
Patients are taught to respond to triggers or heightened symptoms by breaking from “doing” mode and entering “being” mode, thus behaving in a less reactionary way.
“Being” mode is a meditative state of simply existing that offers safe detachment from thoughts and actions.
There are two mindfulness based therapeutic approaches practiced by therapists listed on the Monarch Directory by SimplePractice. One is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), and the other is mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT).
Mindfulness-based stress reduction therapy is a practical eight-week course that teaches people how to cultivate mindfulness through meditation and yoga.
Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) is a complement to CBT that was developed as a therapeutic intervention to treat people with depression.
6. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy (EMDR)
What is it? A therapy that combines memory recall with tracking eyeball activity to re-imprint memories.
Who's it for? People who have experienced trauma and those with post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
EMDR uses bilateral stimulation, directed eye movements and/or alternating left and right taps or vibrations on the knees, shoulders or hands, to help patients access unprocessed memories.
It’s primarily used to treat trauma and PTSD.
Advocates for EMDR believe that when humans experience trauma they are often unable to fully process the information they’re receiving. The result is an unprocessed memory that will continue to trigger negative responses until it is fully processed.
By recalling a traumatic event and opening neural networks simultaneously we pave new roads to these unprocessed memories.
Patients discuss their emotional history with their therapist, recall an “adverse life event,” and undergo bilateral stimulation.
This means that as the patient recalls the life event, therapists might alternate stimulation of the shoulders, knees, and hands between left and right sides of the body, play different tones at intervals, or direct specific eye movements back and forth.
These movements, tones, and taps require patients to learn new, simple behaviors.
When we learn behaviors we form new pathways in our brains called neural networks.
These pathways all connect to one another. By recalling a traumatic event and opening neural networks simultaneously we pave new roads to these unprocessed memories.
The combination of focused recollection and pathway building allows patients to reconnect sections of the brain, then use those connections to get to areas they had previously blocked off due to trauma.
Once processed, the traumatic event is far less likely to cause continued distress when triggers are encountered in the future.
EMDR is not your average talk therapy, and it does require patients to recall disturbing life events. However, it has proven to be quite effective. One study showed that after six sessions, 100% of patients who experienced a single traumatic life event had eliminated PTSD.
Because it works quickly to alleviate symptoms, EMDR can be especially helpful when used in tandem with psychoanalysis or psychodynamic therapy.
See licensed therapists near you who specialize in EMDR.

7. Life coaching
What is it? Career coaching and life coaching are less formalized approach to self improvement
Who's it for? Coaching's beneficial for anyone with concrete life and career goals, rather than mental health concerns and conditions.
Life coaches aren’t necessarily therapists at all.
The role of a life coach is to help clients achieve particular concrete goals, like a promotion at work or a more healthful lifestyle.
Coaches provide encouragement and strategies to help clients jump hurdles in their personal and professional lives.
If having a coach in your corner helps you achieve your goals, go for it. However, you should not seek out a life coach to do a therapist’s work.
While there is some overlap between coaching and therapy, it’s important to note that therapists must study, train, and become licensed to diagnose and treat mental illness.

Coaching requires no license. There’s no formal course of study and no degree or training requirements.
If having a coach in your corner helps you achieve your goals, go for it.
However, you should not seek out a life coach to do a therapist’s work.
Coaches are not a replacement for a licensed mental help therapist, especially if you may be suffering from a mental health condition.
How to find the therapist with the best approach for you
Book a therapy session or a free 15-minute consultation with a therapist.
They’ll help you discover the type of therapy that works best for your needs.
Start by going to Monarch at meetmonarch.com. You can search by entering your location and any particular therapeutic approach and/or specialty.

You can search for therapists who specialize in EMDR, cognitive behavioral therapy, or psychodynamic therapy.
And you can also find therapists who specialize in treating patients with anxiety, depression, or grief.
From there, you can filter results to see therapists who accept your insurance and view their availability to accept new clients.
READ NEXT: What Are Some Good Questions to Ask a Therapist?
Searching for a great therapist? Check out the Monarch Directory by SimplePractice to find licensed therapists near you with availability and online booking.
American Psychological Association. (2017) What is cognitive behavioral therapy? Retrieved from: https://www.apa.org/ptsd-guideline/patients-and-families/cognitive-behavioral
Amano, T., & Toichi, M. (2016). The Role of Alternating Bilateral Stimulation in Establishing Positive Cognition in EMDR Therapy: A Multi-Channel Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study. PLOS ONE, 11(10), e0162735. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162735
GoodTherapy. (2017). Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy. Retrieved from: https://www.goodtherapy.org/learn-about-therapy/types/eye-movement-desensitization-and-reprocessing
Freud, S. (1900). The Interpretation of Dreams. Standard Edition, vols. IV–V. London: Hogarth.
Good Therapy. (2017). Psychoanalysis. Retrieved from: https://www.goodtherapy.org/learn-about-therapy/types/psychoanalysis
Jung, C. G. (1921). Psychological types. The collected works of CG Jung, Vol. 6 Bollingen Series XX.
Lee, Gale K, R.N., M.N., Beaton, Randal D, PhD, E.M.T., & Ensign, Josephine, R.N., PhD. (2003). Eye movement desensitization & reprocessing. Journal of Psychosocial Nursing & Mental Health Services, 41(6), 22-31. Retrieved from: https://journals.healio.com/doi/full/10.3928/0279-3695-20030601-10
Mayo Clinic. (2019). Cognitive behavioral therapy. Retrieved from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cognitive-behavioral-therapy/about/pac-20384610
American Psychological Association. (2019). Mindfulness meditation: A research-proven way to reduce stress. Retrieved from: https://www.apa.org website: https://www.apa.org/topics/mindfulness-meditation
National Alliance on Mental Illness. (2020) Types of mental health professionals. (2020). Retrieved from: https://www.nami.org/About-Mental-Illness/Treatments/Types-of-Mental-Health-Professionals
Personalityresearch.org. (2020). Psychoanalysis: Freud’s revolutionary approach. Retrieved from: http://www.personalityresearch.org/papers/beystehner.html
Psych Central. (1999, May 17). Psychodynamic therapy. Retrieved from: https://psychcentral.com/lib/psychodynamic-therapy/
Psych Central. (2016, May 17). An overview of dialectical behavior therapy. Retrieved from: https://psychcentral.com/lib/an-overview-of-dialectical-behavior-therapy/
SimplePractice. (2019). What’s the difference between therapy, counseling, and coaching? Retrieved from: https://www.simplepractice.com/blog/whats-the-difference-between-therapy-counseling-coaching/